常考手撕代码 一、排序算法 下图是十大经典的排序算法
1.1 冒泡排序 1.1.1 算法思想 重复遍历要排序的序列,依次比较两个元素,如果顺序错误,就交换位置。
1.1.2 算法步骤
比较相邻元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就换位置;
对每一对相邻元素做同样的工作,从开始第一队到结尾的最后一对,这样每次都能找出最大的一个;
针对所有元素重复以上步骤;
重复1-3步,直到排序完成。
1.1.3 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static int [] bubbleSort(int [] nums){ for (int i = nums.length - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--){ for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1 ]){ int temp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[j + 1 ]; nums[j + 1 ] = temp; } } } return nums; }
1.1.4 算法分析
稳定性 :稳定时间复杂度 :最佳:O(n) ,最差:O(n^2), 平均:O(n^2)空间复杂度 :O(1)排序方式 :占用常数内存,不占用额外内存
1.2 选择排序 1.2.1 算法思想 在未排序的序列中找到最小的元素,然后存放在最开始的位置,然后继续从未排序的元素中找最小的,以此类推。
特点就是不论什么顺序的数据,时间复杂度都是O(n^2)。
1.2.2 算法步骤
首先在未排序的序列中找最小的元素,放到序列最开始的位置;
然后在剩下的未排序序列中找最小的元素,放到已排序的序列末尾;
重复第二步,直到排序结束。
1.2.3 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static int [] selectionSort(int [] nums){ for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, index = 0 ; for (int j = i; j < nums.length; j++){ if (nums[j] < min){ min = nums[j]; index = j; } } int temp = nums[index]; nums[index] = nums[i]; nums[i] = temp; } return nums; }
1.2.4 算法分析
稳定性 :不稳定时间复杂度 :最佳:O(n^2) ,最差:O(n^2), 平均:O(n^2)空间复杂度 :O(1)排序方式 :不需要额外空间
1.3 快速排序 1.3.1 算法思想 用到了分治思想,将问题划分为子问题,然后排序子串,最后合并。
通过一趟排序将待排序列分为独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的元素均比另一部分的元素小,则可分别对这两部分子序列继续进行排序,以达到整体有序。
1.3.2 算法步骤
从序列中随机挑选一个元素,作为基准(pivot);
重新排序,将所有比基准值小的元素摆放在基准前面,比基准值大的元素摆放在基准的后面。基准就位于中间位置,这就是分区(partition)。
递归地把小于基准元素的子序列和大于基准元素的子序列进行快排。
1.3.3 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private static void quickSort (int [] nums, int low, int high) { if (low < high){ int position = partition(nums, low, high); quickSort(nums, low, position - 1 ); quickSort(nums, position + 1 , high); } } private static int partition (int [] nums, int low, int high) { int pivot = nums[high]; int index = low; for (int i = low; i < high; i++) { if (nums[i] <= pivot){ swap(nums, i, index); index++; } } swap(nums, index, high); return index; } public static void swap (int [] num, int i, int j) { int temp = num[i]; num[i] = num[j]; num[j] = temp; }
1.3.4 算法分析
稳定性 :不稳定时间复杂度 :最佳:O(nlogn), 最差:O(nlogn),平均:O(nlogn)空间复杂度 :O(nlogn)
1.3.5 优化快排 在快排的基础上加了随机和去重。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private static void quickSort (int [] nums, int low, int high) { if (low < high){ int position = partition(nums, low, high); int leftPosition = position - 1 ; int rightPosition = position + 1 ; while (leftPosition > low && nums[leftPosition] == nums[position]){ leftPosition--; } while (rightPosition < high && nums[rightPosition] == nums[position]){ rightPosition++; } quickSort(nums, low, leftPosition); quickSort(nums, rightPosition, high); } } private static int partition (int [] nums, int low, int high) { int randomIndex = low + (int )Math.random() *(high - low + 1 ); swap(nums, high, randomIndex); int pivot = nums[high]; int index = low; for (int i = low; i < high; i++){ if (nums[i] <= pivot){ swap(nums, i, index); index++; } } swap(nums, index, high); return index; } private static void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; }
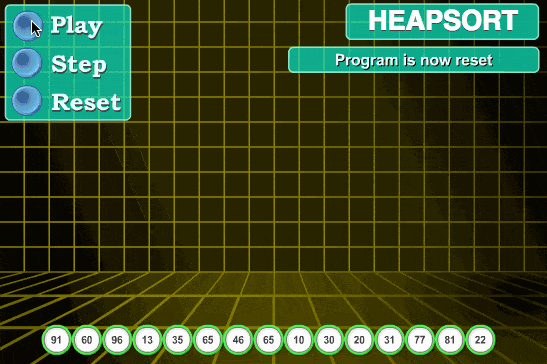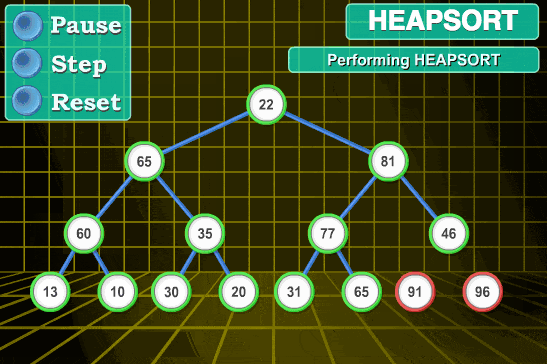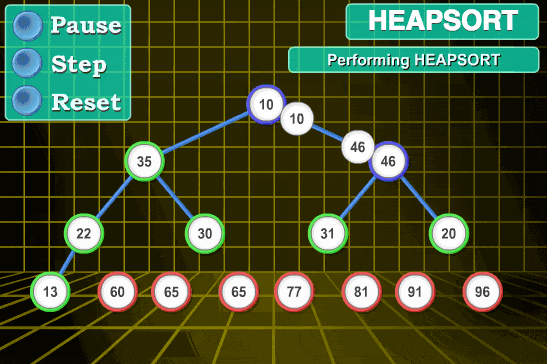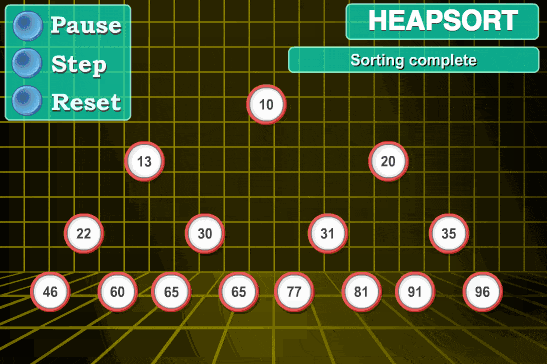
1.4 堆排序 1.4.1 算法思想 利用堆的数据结构特性,即子节点的值总是小于(或大于)其父节点。
1.4.2 算法步骤
将初始待排序列构建成大顶堆,次堆为初始的无序区。
将堆顶元素 R[1] 与最后一个元素 R[n] 交换,此时得到新的无序区 (R1, R2, ……, Rn-1) 和新的有序区 (Rn), 且满足 R[1, 2, ……, n-1]<=R[n];
由于交换后的新堆R[1]可能违反堆的性质,因此需要对当前无序区重新调整,然后再次将R[1]与无序区最后一个元素交换,得到新的无序区和有序区。不断重复,直到排序过程完成。
1.4.3 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public static int heapLen;public static int [] heapSort(int [] nums) { heapLen = nums.length; buildMaxHeap(nums); for (int i = nums.length - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { swap(nums, 0 , i); heapLen--; heapify(nums, 0 ); } return nums; } private static void buildMaxHeap (int [] nums) { for (int i = nums.length / 2 - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { heapify(nums, i); } } private static void heapify (int [] nums, int i) { int left = 2 * i + 1 ; int right = 2 * i + 2 ; int largest = i; if (left < heapLen && nums[left] > nums[largest]){ largest = left; } if (right < heapLen && nums[right] > nums[largest]){ largest = right; } if (largest != i){ swap(nums, i, largest); heapify(nums, largest); } } private static void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; }
1.4.4 算法分析
稳定性 :不稳定时间复杂度 :最佳:O(nlogn), 最差:O(nlogn), 平均:O(nlogn)空间复杂度 :O(1)
1.5 归并排序 1.5.1 算法思想 也是采用分治算法的典型,将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列,也称为2路归并。代价是需要额外的内存空间。
1.5.2 算法步骤
如果输入只有一个元素,则直接返回,否则将长度为n的输入序列分为两个长度为n/2的子序列;
分别对这两个子序列进行归并排序,使子序列变为有序状态;
设定两个指针,分别指向两个已经排序子序列的起始位置;
比较两个指针所指向的元素,选择相对较小的放入到合并空间,并移动指针;
重复第3步和第4步,直到全部有序
1.5.3 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 private static void mergeSort (int [] nums, int low, int high) { if (low < high){ int mid = (low + high) / 2 ; mergeSort(nums, low, mid); mergeSort(nums, mid + 1 , high); merge(nums, low, mid, high); } } private static void merge (int [] nums, int low, int mid, int high) { int [] arr = new int [high - low + 1 ]; int index = 0 ; int left = low, right = mid + 1 ; while (left <= mid && right <= high){ if (nums[left] < nums[right]){ arr[index++] = nums[left++]; }else { arr[index++] = nums[right++]; } } while (left <= mid){ arr[index++] = nums[left++]; } while (right <= high){ arr[index++] = nums[right++]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { nums[i + low] = arr[i]; } } }
1.5.4 算法分析
稳定性 :稳定时间复杂度 :最佳:O(nlogn), 最差:O(nlogn), 平均:O(nlogn)空间复杂度 :O(n)
二、红黑树 2.1 红黑树性质 红黑树是一种近似平衡的二叉查找树 ,但并非绝对平衡,但是可以保证任何一个节点 的左右子树的高度差不会超过二者中较低的那个的一倍 。
特点:
每个节点要么是黑色,要么是红色。
根节点是黑色。
每个叶子节点(NULL)是黑色。
每个红色结点的两个子结点一定都是黑色。
任意一结点到每个叶子结点的路径都包含数量相同的黑结点。
红黑树为什么能自平衡?
红黑树总是通过旋转和变色达到自平衡 。
左旋 :以某个结点作为支点(旋转结点),其右子结点变为旋转结点的父结点,右子结点的左子结点变为旋转结点的右子结点,左子结点保持不变。
右旋 :以某个结点作为支点(旋转结点),其左子结点变为旋转结点的父结点,左子结点的右子结点变为旋转结点的左子结点,右子结点保持不变。
变色 :结点的颜色由红变黑或由黑变红。
左旋 只影响旋转结点和其右子树 的结构,把右子树的结点往左子树挪了。右旋 只影响旋转结点和其左子树 的结构,把左子树的结点往右子树挪了。
2.2 红黑树查找
从根结点开始查找,把根结点设置为当前结点;
若当前结点为空,返回null;
若当前结点不为空,用当前结点的key跟查找key作比较;
若当前结点key等于查找key,那么该key就是查找目标,返回当前结点;
若当前结点key大于查找key,把当前结点的左子结点设置为当前结点,重复步骤2;
若当前结点key小于查找key,把当前结点的右子结点设置为当前结点,重复步骤2;
2.3 红黑树插入 首先找插入的位置,然后再自平衡。
从根结点开始查找;
若根结点为空,那么插入结点作为根结点,结束。
若根结点不为空,那么把根结点作为当前结点;
若当前结点为null,返回当前结点的父结点,结束。
若当前结点key等于查找key,那么该key所在结点就是插入结点,更新结点的值,结束。
若当前结点key大于查找key,把当前结点的左子结点设置为当前结点,重复步骤4;
若当前结点key小于查找key,把当前结点的右子结点设置为当前结点,重复步骤4;
情况1:红黑树为空树 直接把插入的节点作为根节点,并把该节点设为黑色。
情况2:插入节点的key已经存在
把I设为当前节点的颜色
更新当前结点的值为插入节点的值
情况3:插入节点的父节点为黑节点 这种情况不会影响红黑树平衡,直接插入即可。
情况4:插入节点的父节点为红节点 情况4.1:叔叔节点存在且为红节点 因为其祖父节点肯定存在,且肯定为黑色,所以此时颜色的情况为:黑红红
那么最简单的处理方法就是改为:红黑红
情况4.2:叔叔节点不存在或为黑色节点,且父节点是祖父节点的左子节点
插入节点是其父节点的左子节点
插入节点是其父节点的右子节点
对P进行左旋 把P设置为插入结点,得到情景4.2.1 进行情景4.2.1的处理
情况4.3:叔叔节点不存在或为黑色节点,且父节点是祖父节点的右子节点
插入节点是父节点的右子节点
插入节点是父节点的左子节点
对P进行右旋 把P设置为插入结点,得到情景4.3.1 进行情景4.3.1的处理
2.4 红黑树删除 情况1:替换节点是红色 颜色变为删除节点的颜色
情况2:替换节点是黑色 情况2.1:替换节点是其父节点的左子节点
替换节点的兄弟节点是红节点
将S设为黑色 将P设为红色 对P进行左旋,得到情景2.1.2.3 进行情景2.1.2.3的处理
替换节点的兄弟节点是黑节点
替换节点的兄弟节点的右子节点是红节点,左子节点任意颜色
直接向右子树“借”个红结点来补充黑结点
将S的颜色设为P的颜色 将P设为黑色 将SR设为黑色 对P进行左旋
替换节点的兄弟节点的右子节点为黑色,左子节点为红色
向兄弟子树借个红结点过来
将S设为红色 将SL设为黑色 对S进行右旋,得到情景2.1.2.1 进行情景2.1.2.1的处理
替换节点的兄弟节点的子节点都为黑色
把兄弟结点设为红色,再把父结点当作替代结点,自底向上处理,去找父结点的兄弟结点去“借”
将S设为红色 把P作为新的替换结点 重新进行删除结点情景处理
情况2.2 替换节点是其父节点的右子节点
替换节点的兄弟节点是红节点
将S设为黑色 将P设为红色 对P进行右旋,得到情景2.2.2.3 进行情景2.2.2.3的处理
替换节点的兄弟节点是黑节点
替换节点的兄弟节点的左子节点是红节点,右子节点任意颜色
将S的颜色设为P的颜色 将P设为黑色 将SL设为黑色 对P进行右旋
替换节点的兄弟节点的左子节点是黑节点,右子节点是红节点
将S设为红色 将SR设为黑色 对S进行左旋,得到情景2.2.2.1 进行情景2.2.2.1的处理
替换节点的兄弟节点的子节点都是黑色
将S设为红色 把P作为新的替换结点 重新进行删除结点情景处理
综上,红黑树删除后自平衡的处理可以总结为:
自己能搞定的自消化(情景1)
自己不能搞定的叫兄弟帮忙(除了情景1、情景2.1.2.3和情景2.2.2.3)
兄弟都帮忙不了的,通过父母,找远方亲戚(情景2.1.2.3和情景2.2.2.3)
三、常考手撕 直接看这个网站CodeTop企业题库
3.1 无重复字符的最长子串 3. 无重复字符的最长子串 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
1 2 3 输入: s = "abcabcbb" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
3.1.1 方法一:HashSet+滑动窗口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { if (s.length() <= 1 ){ return s.length(); } int ans = 0 , index = 0 ; HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ char c = s.charAt(i); if (set.contains(c)){ ans = Math.max(ans, set.size()); while (s.charAt(index) != c){ set.remove(s.charAt(index)); index++; } set.remove(s.charAt(index)); index++; } set.add(c); } return Math.max(ans, set.size()); } }
3.1.2 方法二:双指针+滑动窗口+字典 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { int ans = 0 , index = 0 ; int [] dict = new int [128 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 128 ; i++){ dict[i] = -1 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ index = Math.max(index, dict[s.charAt(i)] + 1 ); ans = Math.max(ans, i - index + 1 ); dict[s.charAt(i)] = i; } return ans; } }
3.2 反转链表 206. 反转链表 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
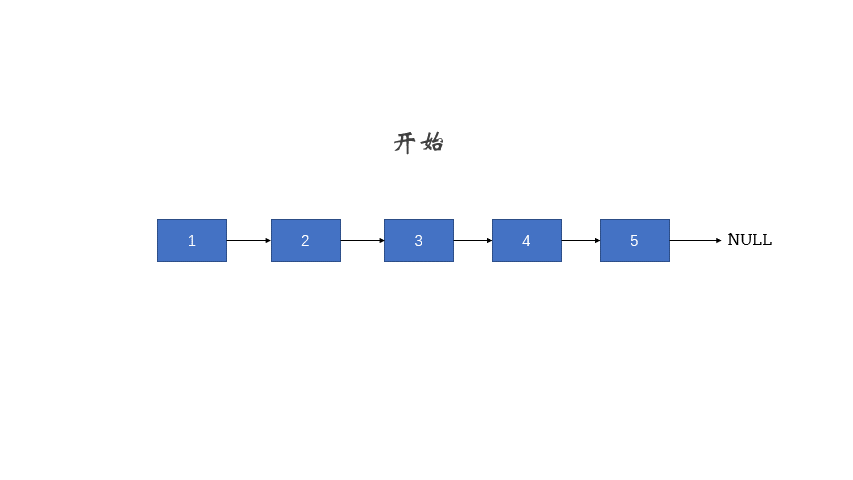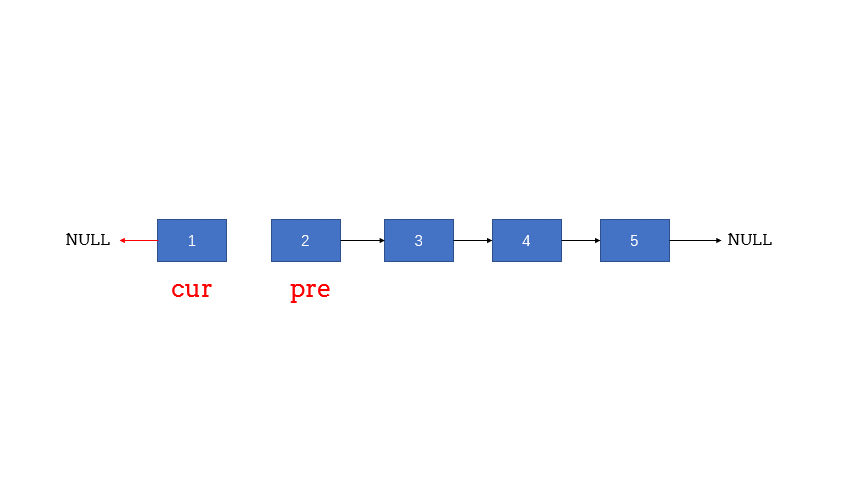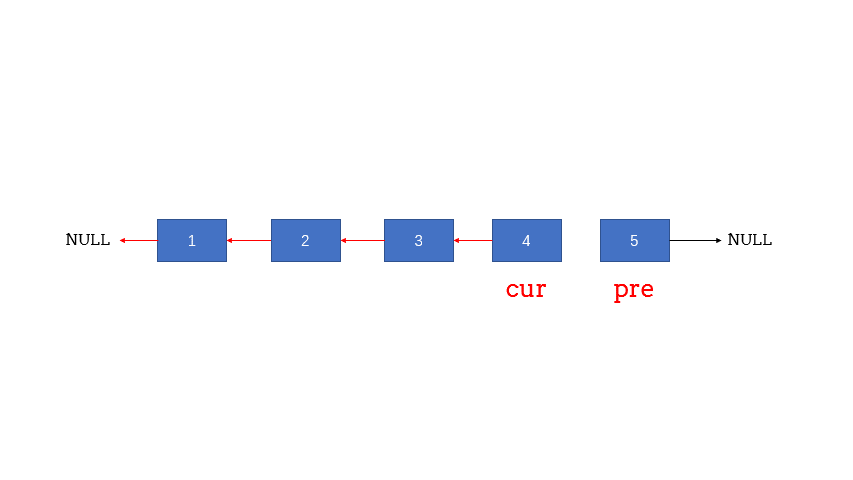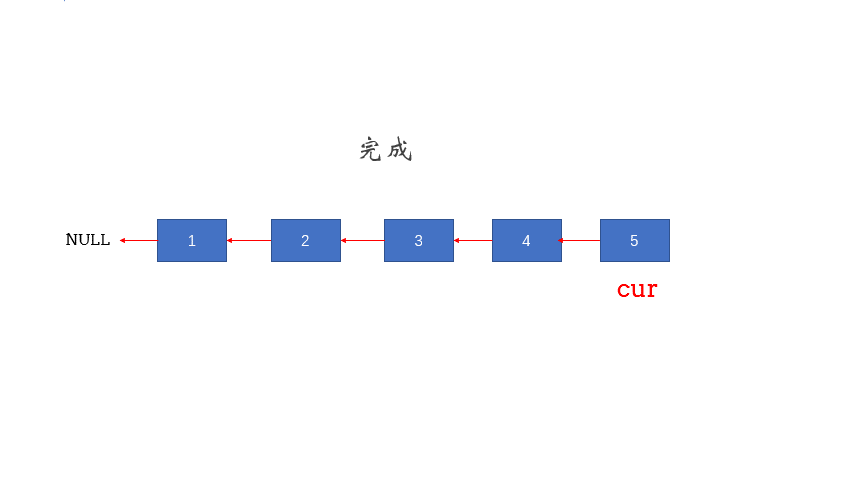
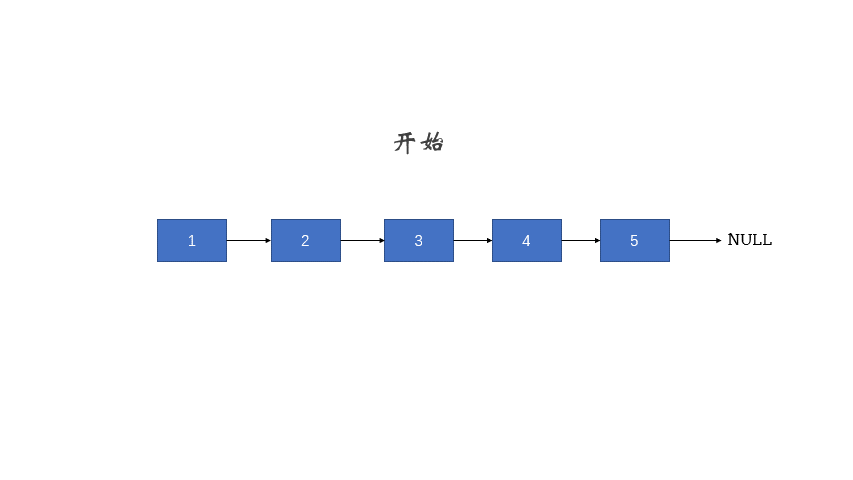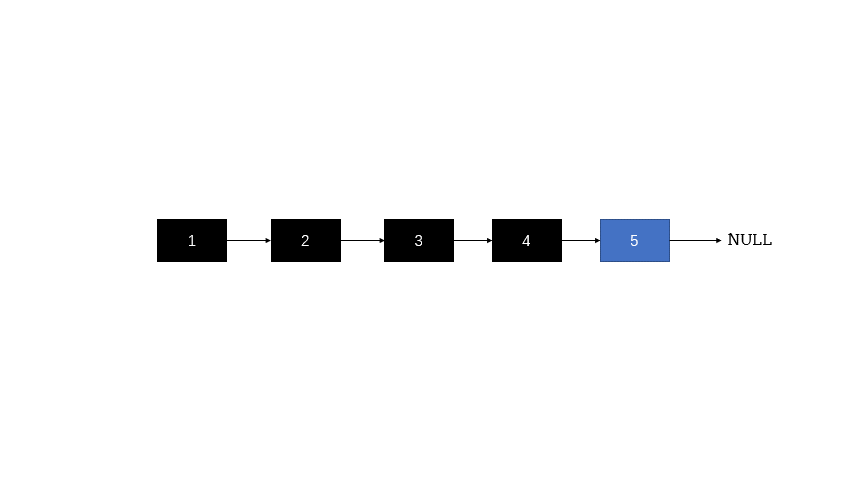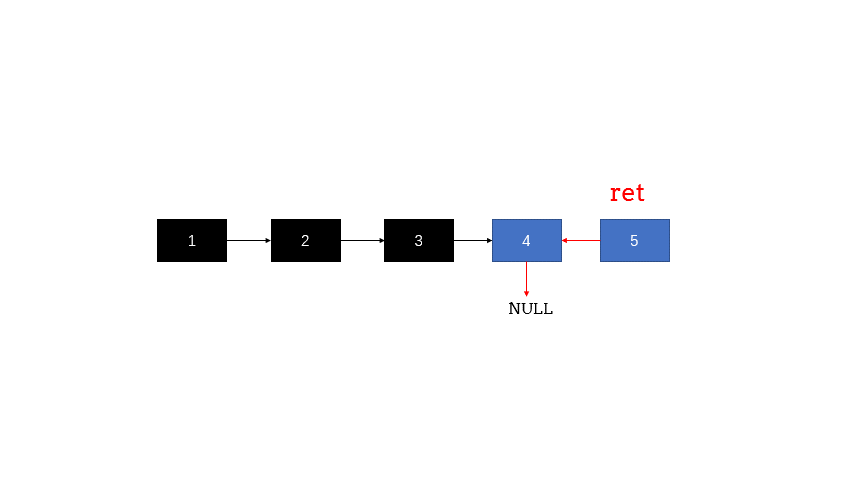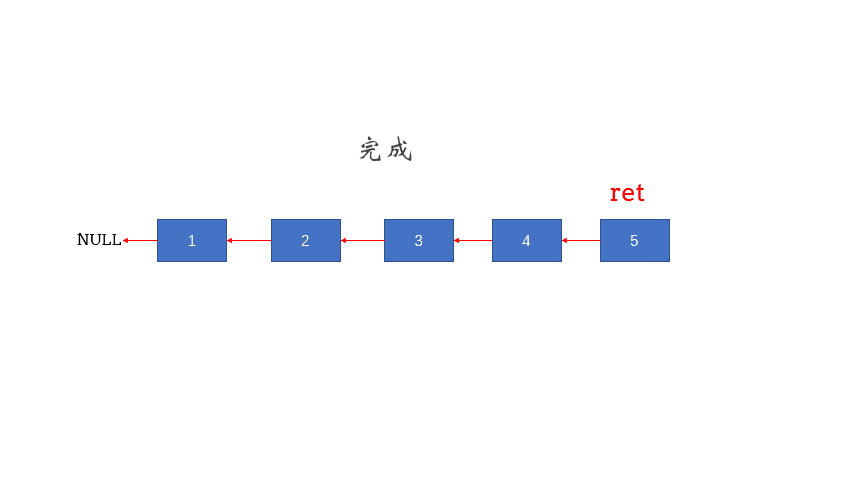
3.2.1 方法一:迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head == null ){ return null ; } ListNode p = head, q = null ; while (p != null ){ ListNode temp = p.next; p.next = q; q = p; p = temp; } return q; } }
3.2.2 方法二:递归法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ){ return head; } ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null ; return newHead; } }
3.2.3 方法三:头插法(优化迭代) 该方法比常规的迭代法内存消耗要低很多,属于优化版的迭代法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ){ return head; } ListNode newHead = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode p = head, q = null ; while (p != null ){ q = p.next; p.next = newHead.next; newHead.next = p; p = q; } return newHead.next; } }
3.3 LRU缓存 146. LRU 缓存 - 力扣(Leetcode)
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity) 以 正整数 作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字 key 已经存在,则变更其数据值 value ;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组 key-value 。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过 capacity ,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 输入 ["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"] [[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]] 输出 [null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4] 解释 LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2); lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1} lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1 lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3} lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3} lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到) lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3 lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
3.3.1 方法一:LinkedHashMap(不推荐) 如果实在不记得怎么写,可以取巧用LinkedHashMap来实现,因为LinkedHashMap的特性就是双向链表+HashMap,但是面试官想考的并不是LinkedHashMap。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class LRUCache { private int cap; private Map<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap <>(); public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .cap = capacity; } public int get (int key) { if (map.keySet().contains(key)){ int value = map.get(key); map.remove(key, value); map.put(key, value); return value; } return -1 ; } public void put (int key, int value) { if (map.keySet().contains(key)){ map.remove(key, map.get(key)); }else if (map.size() == cap){ Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator(); if (iterator.hasNext()) { iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); } } map.put(key, value); } }
3.3.2 方法二:双向链表+HashMap(推荐) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 class LRUCache { class DLinkedNode { public int key; public int value; public DLinkedNode pre; public DLinkedNode next; public DLinkedNode () {} public DLinkedNode (int key, int value) { this .key = key; this .value = value; } } public void removeNode (DLinkedNode node) { node.next.pre = node.pre; node.pre.next = node.next; } public void addToHead (DLinkedNode node) { head.next.pre = node; node.next = head.next; head.next = node; node.pre = head; } public void moveToHead (DLinkedNode node) { removeNode(node); addToHead(node); } public DLinkedNode removeLastNode () { DLinkedNode resNode = tail.pre; removeNode(resNode); return resNode; } public HashMap<Integer, DLinkedNode> map = new HashMap <>(); public int mapCap; public int size; public DLinkedNode head, tail; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .size = 0 ; this .mapCap = capacity; head = new DLinkedNode (); tail = new DLinkedNode (); head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; } public int get (int key) { DLinkedNode node = map.get(key); if (node != null ){ moveToHead(node); return node.value; }else { return -1 ; } } public void put (int key, int value) { DLinkedNode node = map.get(key); if (node == null ){ node = new DLinkedNode (key, value); map.put(key, node); addToHead(node); size++; if (size > mapCap){ DLinkedNode lastNode = removeLastNode(); map.remove(lastNode.key); size--; } }else { moveToHead(node); node.value = value; } } }
3.4 数组中第k大的元素 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。
请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
1 2 输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 输出: 5
3.4.1 方法一:随机快排 快排的时间复杂度不符合要求的O(n),必须得用随机快排。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { quickSort(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); return nums[nums.length - k]; } public void quickSort (int [] nums, int low, int high) { if (low < high){ int position = partition(nums, low, high); quickSort(nums, low, position - 1 ); quickSort(nums, position + 1 , high); } } public int partition (int [] nums, int low, int high) { int randomIndex = low + (int )Math.random()*(high - low + 1 ); swap(nums, randomIndex, high); int povit = nums[high]; int index = low; for (int i = low; i < high; i++){ if (nums[i] <= povit){ swap(nums, i, index); index++; } } swap(nums, high, index); return index; } public void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } }
3.4.2 方法二:堆排序 堆排序其实不符合题中要求的O(n),但是面试官经常会问一句如果用堆排序该怎么做。可以维护一个只有k个元素的小根堆,堆顶元素就是答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { int [] arr = new int [k]; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { arr[i] = nums[i]; } buildHeap(arr, k - 1 ); for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] > arr[0 ]) { arr[0 ] = nums[i]; heapify(arr, k - 1 , 0 ); } } return arr[0 ]; } private void buildHeap (int [] nums, int n) { for (int i = n / 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { heapify(nums, n, i); } } private void heapify (int [] nums, int n, int i) { while (true ) { int minPos = i; int left = 2 * i + 1 ; int right = left + 1 ; if (left <= n && nums[minPos] > nums[left]){ minPos = left; } if (right <= n && nums[minPos] > nums[right]){ minPos = right; } if (minPos == i){ break ; } swap(nums, i, minPos); i = minPos; } } private void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } }
3.4.3 方法三:优先队列 其实本质上还是小根堆。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { PriorityQueue<Integer> minTree = new PriorityQueue <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ minTree.add(nums[i]); if (minTree.size() > k){ minTree.poll(); } } return minTree.peek(); } }
3.5 K个一组翻转链表 25. K 个一组翻转链表 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
3.5.1 方法一:尾插法 先统计链表长度,然后第一重循环看一共要翻转几次,第二重循环控制每次翻转要翻转k-1次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { int listLength = 0 ; ListNode newHead = new ListNode (0 ), p = newHead, q = head, temp; newHead.next = head; while (head != null ){ listLength++; head = head.next; } head = newHead.next; for (int i = 0 ; i < listLength / k; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < k - 1 ; j++){ temp = q.next; q.next = temp.next; temp.next = p.next; p.next = temp; } p = q; q = p.next; } return newHead.next; } }
3.5.2 方法二:栈 因为栈的特性就是先进后出,每次压入k个节点,那么弹出的顺序就是翻转后的顺序。
只不过需要注意,如果最后不足k个节点,就不翻转链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { Deque<ListNode> stack = new ArrayDeque <>(); ListNode newHead = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode p = newHead; while (true ){ int count = 0 ; ListNode q = head; while (q != null && count < k){ stack.add(q); q = q.next; count++; } if (count != k){ p.next = head; break ; } while (!stack.isEmpty()){ p.next = stack.pollLast(); p = p.next; } p.next = q; head = q; } return newHead.next; } }
3.5.3 方法三:递归法
找到待翻转的k个节点(如果结点数少于k的话就不用翻转);
对k个节点进行翻转操作,并返回反转后的头结点(反转的区间为左开右闭,所以本轮操作的尾结点就是下一轮操作的头结点);
对下一轮k个节点同样进行翻转操作;
将上一轮翻转后的尾结点指向下一轮翻转后的头结点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { ListNode tail = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { if (tail == null ) { return head; } tail = tail.next; } ListNode newHead = reverse(head, tail); head.next = reverseKGroup(tail, k); return newHead; } private ListNode reverse (ListNode head, ListNode tail) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode next = null ; while (head != tail) { next = head.next; head.next = pre; pre = head; head = next; } return pre; } }
3.6 三数之和 15. 三数之和 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请
你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意: 答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] 输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] 解释: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。 nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。 nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。 不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。 注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
3.6.1 方法一:双指针+内部去重 这题想法不难,难的是如何去重。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> ansList = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); if (nums[0 ] > 0 || nums[nums.length - 1 ] < 0 ){ return ansList; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 2 ; i++){ if (nums[i] > 0 ){ return ansList; } if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]){ continue ; } int left = i + 1 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left < right){ int target = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (target < 0 ){ left++; }else if (target > 0 ){ right--; }else { List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList <>(); temp.add(nums[i]); temp.add(nums[left]); temp.add(nums[right]); ansList.add(temp); while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]){ left++; } while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]){ right--; } left++; right--; } } } return ansList; } }
3.6.2 方法二:双指针+HashSet去重 思路是一样的,只不过使用HashSet去重,时间复杂度和空间复杂度要差很多,就不写代码了。
3.7 手撕快排 912. 排序数组 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给你一个整数数组 nums,请你将该数组升序排列。
优化过的快排:随机选取基准元素+去重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { public int [] sortArray(int [] nums) { quickSort(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); return nums; } public void quickSort (int [] nums, int low, int high) { if (low < high){ int position = partition(nums, low, high); int leftPosition = position - 1 ; int rightPosition = position + 1 ; while (leftPosition > low && nums[position] == nums[leftPosition]){ leftPosition--; } while (rightPosition < high && nums[position] == nums[rightPosition]){ rightPosition++; } quickSort(nums, low, leftPosition); quickSort(nums, rightPosition, high); } } public int partition (int [] nums, int low, int high) { int randomIndex = low + (int )Math.random() * (high - low + 1 ); swap(nums, randomIndex, high); int pivot = nums[high]; int index = low; for (int i = low; i < high; i++){ if (nums[i] <= pivot){ swap(nums, index, i); index++; } } swap(nums, high, index); return index; } public void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } }
3.8 最大子数组和 53. 最大子数组和 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
子数组 是数组中的一个连续部分。
1 2 3 输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] 输出:6 解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。
3.8.1 方法一:DP法 每次操作有两种可能:
前面所求最大元素max加上当前元素nums[i];
不带前面玩,只用当前元素nums[i]。
然后每次完毕之后,用ans保存最大的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ){ return nums[0 ]; } int max = 0 ; int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ max = Math.max(nums[i] + max, nums[i]); ans = Math.max(max, ans); } return ans; } }
3.8.2 方法二:贪心法 相当于把所有结果加起来,如果sum小于0,那说明前面的都不作数,重新将sum置为0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxSubAray (int [] nums) { int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int numsSize = nums.length; int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize; i++){ sum += nums[i]; result = Math.max(result, sum); if (sum < 0 ){ sum = 0 ; } } return result; } }
3.8.3 方法三:分治法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution { public int maxSubAray (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length <= 0 ) return 0 ; int len = nums.length; return getInfo(nums, 0 , len - 1 ).mSum; } class wtevTree { int lSum; int rSum; int iSum; int mSum; wtevTree(int l, int r, int i, int m) { lSum = l; rSum = r; iSum = i; mSum = m; } } wtevTree pushUp (wtevTree leftT, wtevTree rightT) { int l = Math.max(leftT.lSum, leftT.iSum + rightT.lSum); int r = Math.max(leftT.rSum + rightT.iSum, rightT.rSum); int i = leftT.iSum + rightT.iSum; int m = Math.max(leftT.rSum + rightT.lSum, Math.max(leftT.mSum, rightT.mSum)); return new wtevTree (l, r, i, m); } wtevTree getInfo (int [] nums, int left, int right) { if (left == right) return new wtevTree (nums[left], nums[left], nums[left], nums[left]); int mid = (left + right) >> 1 ; wtevTree leftT = getInfo(nums, left, mid); wtevTree rightT = getInfo(nums, mid + 1 , right); return pushUp(leftT, rightT); } }
3.9 合并两个有序链表 21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(Leetcode)
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
1 2 输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
3.9.1 方法一:迭代法 没什么说的,创建一个新节点head,然后连接上就行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode head = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode p = head; while (list1 != null && list2 != null ){ if (list1.val <= list2.val){ p.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; }else { p.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } p = p.next; } if (list1 == null ){ p.next = list2; }else { p.next = list1; } return head.next; } }
3.9.2 方法二:递归法 递归连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { if (list1 == null ){ return list2; } if (list2 == null ){ return list1; } if (list1.val <= list2.val){ list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2); return list1; }else { list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next); return list2; } } }
3.10 两数之和 1. 两数之和 - 力扣(Leetcode)
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
进阶: 你可以想出一个时间复杂度小于 O($n^2$)的算法吗?
1 2 3 输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[0,1] 解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
3.10.1 方法一:暴力双循环 没什么好说的,暴力双循环,时间复杂度O($n^2$)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { int [] ans = new int [2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ for (int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.length; j++){ if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target){ ans[0 ] = i; ans[1 ] = j; } } } return ans; } }
3.10.2 方法二:HashMap 因为结果要求返回的是下标,所以不能用排序改变元素位置。
只能通过HashMap来保存值和索引位置,map的key用来保存target - nums[i]的值,这样一来,只需要看后面的元素是否有等于这个差值的。
如果有的话,那就说明找到了这两个值的位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { int [] ans = new int [2 ]; HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ int temp = target - nums[i]; if (!map.containsKey(nums[i])){ map.put(temp, i); }else { ans[0 ] = i; ans[1 ] = map.get(nums[i]); break ; } } return ans; } }
时间复杂度为O(n)。
四、单例模式 4.1 懒汉式单例 特点:当需要使用对象的时候才进行实例化,需要考虑线程安全的问题,因此要加锁,用时间换空间。
传统实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Singleton { private Singleton () {} private static Singleton LazyMan; public static synchronized Singleton getInstance () { if (LazyMan == null ) { LazyMan = new Singleton (); } return LazyMan; } }
优化实现:
传统实现方式中,每次获取实例都要被synchronized关键字串行化 (即使已经生成了实例)。
而我们加锁的目的是为了防止生成多个实例 ,因此只需对生成实例的代码加锁,生成实例后,可支持并发访问,提高了性能。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Singleton { private Singleton () {} private volatile static Singleton LazyMan; public static Singleton getInstance () { if (LazyMan == null ) { synchronized (Singleton.class) { if (LazyMan == null ) { LazyMan = new Singleton (); } } } return LazyMan; } }
由于检查了两次对象是否已实例化,该方法又称“双检锁” ,能够同时保证性能及线程安全。
4.2 饿汉式单例 特点:类加载时便实例化对象,拿空间换时间。
传统实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Singleton { private Singleton () {} private static Singleton Hungry = new Singleton (); public static Singleton getInstance () { return Hungry; } }
优化实现:
传统实现方式中,由于类加载时就实例化对象,因此当我们调用静态方法时,也会进行实例化,从而导致空间的浪费。
由于静态内部类中的对象不会默认加载,直到调用了该内部类的方法,因此可用静态内部类封装静态实例变量 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Singleton { private Singleton () {} private static class SingletonHolder { private static Singleton Hungry = new Singleton (); } public static Singleton getInstance () { return SingletonHolder.Hungry; } }
五、多线程异步打印ABC 5.1 synchronized + wait/notify 5.1.1 三个线程轮流打印A、B、C,1次 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class Main { private int num; private static Object Lock = new Object (); private void printABC (String name, int targetNum) { synchronized (Lock){ while (num % 3 != targetNum){ try { Lock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } num++; System.out.print(name); Lock.notifyAll(); } } public static void main (String[] args) { Main main = new Main (); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC("A" , 0 ); }, "ThreadA" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC("B" , 1 ); }, "ThreadB" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC("C" , 2 ); }, "ThreadC" ).start(); } }
基本思路:
让A、B、C三个线程同时启动,因为num的初始值是0,所以线程B、C拿到Lock之后会进入循环;
然后B、C线程调用wait()方法进入等待;
A线程不会进入循环,所以可以让num++,并且打印A;
打印完后,执行notifyAll()方法,让其他阻塞的线程苏醒,然后继续循环打印。
5.1.2 三个线程轮流打印A、B、C,10次 整体思路与上面一样,只不过在外面加了个循环而已。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class Main { private int num; private static Object Lock = new Object (); private void printABC (String threadName, int targetNum) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { synchronized (Lock){ while (num % 3 != targetNum){ try { Lock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } num++; System.out.print(threadName); Lock.notifyAll(); } } } public static void main (String[] args) { Main main = new Main (); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC("A" , 0 ); }, "ThreadA" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC("B" , 1 ); }, "ThreadB" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC("C" , 2 ); }, "ThreadC" ).start(); } }
5.1.3 两个线程轮流打印1-20内的奇偶数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class Main { private int num = 1 ; private static Object Lock = new Object (); private void printOddEven () { synchronized (Lock){ while (num <= 20 ){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" ); System.out.println(num++); try { Lock.notifyAll(); Lock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } Lock.notifyAll(); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Main main = new Main (); new Thread (() -> { main.printOddEven(); }, "Odd" ).start(); Thread.sleep(10 ); new Thread (() -> { main.printOddEven(); }, "Even" ).start(); } }
5.1.4 N个线程轮流打印1-maxNum内的数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class Main { private int num; private static Object Lock = new Object (); private int maxNum = 20 ; private int N = 4 ; private void printMaxNum (int targetNum) { while (true ){ synchronized (Lock){ while (num % N != targetNum){ if (num >= maxNum){ break ; } try { Lock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (num >= maxNum){ break ; } num++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + num); Lock.notifyAll(); } } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Main main = new Main (); new Thread (() -> { main.printMaxNum(0 ); }, "T1" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printMaxNum(1 ); }, "T2" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printMaxNum(2 ); }, "T3" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printMaxNum(3 ); }, "T4" ).start(); } }
5.2 join() join()方法可以指定线程执行的顺序,无论谁先执行,最后的顺序都是1-2-3。
还是那道题,三个线程轮流打印ABC十次
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class Main { static class printABC implements Runnable { private Thread beforeThread; public printABC (Thread beforeThread) { this .beforeThread = beforeThread; } @Override public void run () { if (beforeThread != null ){ try { beforeThread.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { Thread T1 = new Thread (new printABC (null ), "A" ); Thread T2 = new Thread (new printABC (T1), "B" ); Thread T3 = new Thread (new printABC (T2), "C" ); T1.start(); T2.start(); T3.start(); Thread.sleep(10 ); } } }
5.3 Lock 该方法更容易理解,不管哪个线程拿到锁,只有符合条件的才能打印。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Main { private static int num; private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock (); private void printABC (int targetNum) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; ) { lock.lock(); if (num % 3 == targetNum){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName()); num++; i++; } lock.unlock(); } } public static void main (String[] args) { Main main = new Main (); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC(0 ); }, "A" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC(1 ); }, "B" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { main.printABC(2 ); }, "C" ).start(); } }
六、AMC模式输入代码 6.1 数组建链表
第一行输入n,表示链表中的元素个数;
第二行输入n个元素,表示链表中节点的值;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class ListNode { int value; ListNode next; public ListNode () {}; public ListNode (int value) { this .value = value; } } public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int n = sc.nextInt(); int [] nums = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { nums[i] = sc.nextInt(); } ListNode head = buildList(nums); while (head != null ){ System.out.print(head.value); head = head.next; } } public static ListNode buildList (int [] arr) { ListNode head = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode p = head; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { ListNode q = new ListNode (arr[i]); p.next = q; p = p.next; } return head.next; } }
6.2 数组建二叉树
第一行输入n,二叉树中一共有多少个节点;
第二行输入n个元素,表示层序遍历二叉树的结果,-1表示节点为空;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class TreeNode { int value; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; public TreeNode (int value) { this .value = value; } } public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int n = sc.nextInt(); int [] nums = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { nums[i] = sc.nextInt(); } TreeNode root = buildTree(nums); } public static TreeNode buildTree (int [] arr) { if (arr == null || arr.length == 0 ){ return null ; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode (arr[0 ]); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); for (int i = 1 ; i < arr.length; i += 2 ) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (arr[i] != -1 ){ node.left = new TreeNode (arr[i]); queue.offer(node.left); } if (i + 1 < arr.length && arr[i + 1 ] != -1 ){ node.right = new TreeNode (arr[i + 1 ]); queue.offer(node.right); } } return root; } }
6.3 输入边建二叉树
第一行输入一个正整数n,代表节点的数量;
接下来的n - 1行,每行输入两个正整数a,b,代表节点a和节点b有一条边连接;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; public TreeNode (int val) { this .val = val; } } public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int n = scanner.nextInt(); TreeNode[] nodes = new TreeNode [n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { nodes[i] = new TreeNode (i); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++) { int u = scanner.nextInt(); int v = scanner.nextInt(); if (nodes[u].left == null ) { nodes[u].left = nodes[v]; } else { nodes[u].right = nodes[v]; } } TreeNode root = nodes[1 ]; } }
6.4 输入边建二叉树(以链表形式存储) 这种方式存的是边,并没有真的建立二叉树。
第一行输入一个正整数n,代表节点的数量;
接下来的n - 1行,每行输入两个正整数a,b,代表节点a和节点b有一条边连接;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import java.util.*;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in); int n = sc.nextInt(); List<List<Integer>> edge = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++) { edge.add(new ArrayList <>()); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++) { int a = sc.nextInt(); int b = sc.nextInt(); edge.get(a).add(b); edge.get(b).add(a); } for (int i = 0 ; i < edge.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < edge.get(i).size(); j++) { System.out.print(edge.get(i).get(j) + " " ); } System.out.println(); } } }